| Leccinum crocipodium (Letell.) Watling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
The cap is yellow, turning brown with age, lemon-yellow when young, olive-yellow then yellow-brown, fleshy, hemispherical at first, then convex. The cap surface is downy, slightly viscid when young or in wet weather, then cracked, embossed, fragmented into large darker patches, showing between them the yellow skin;. The cap margin is exceeding, overhanging the tubes then retracting with age to show the tubes. The stem is tough, full, long and firm, rough because of the small longitudinally arranged scales on its surface. It is egg-shaped at first when young, then swollen or spindle-shaped, tapering at the top, rather thick. The background colour of the stem is sulphur yellow, turning brown with age; The scales on the stem also become red-brown then grey with age. The mycelium at the base is yellowish-grey.. The flesh is thick, firm at first then soft, the stem being fibrous. It is pale yellow, turning red quickly when in contact with air, then turning grey and eventually blackening (in about a quarter of an hour); its taste is faint or mild; the odour is weak to pleasant; The tubes are free, thin, long (12-26mm). They are lemon yellow then ochre to brown, turning brown when cut and exposed to air. The pores are small, round, white then yellow then brown, turning brown when pressed. The spore print is yellow-brown. It grows in broad-leaved woods, with oak and beech. The fruiting period takes place from June to November.
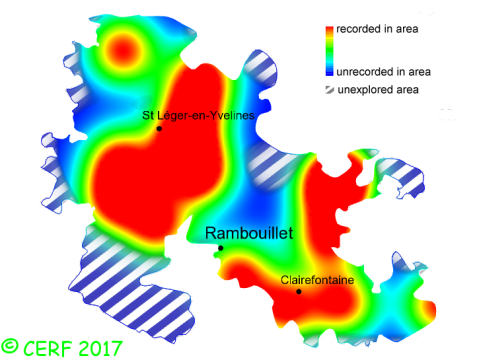
Chemical tests : The flesh becomes : olive green when in contact with ammonia, pale olivaceous green when in contact with iron sulphate, brick-red when in contact with formaldehyde. Distinctive features : yellow shades; cap fragmented into large brownish segments; tough stem covered with small yellowish-brown scales; white pores, tuning eventually yellow with age; flesh turning red then black when exposed to air Leccinum crocipodium is occasional and widely present in the forest of Rambouillet, and is infrequent, more generally speaking . | ||
|
page updated on 14/01/18